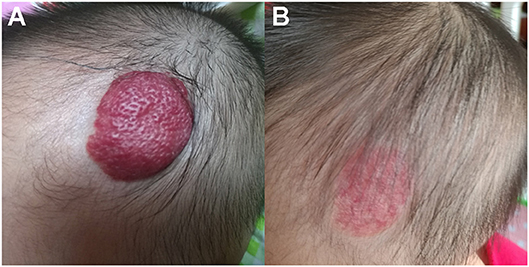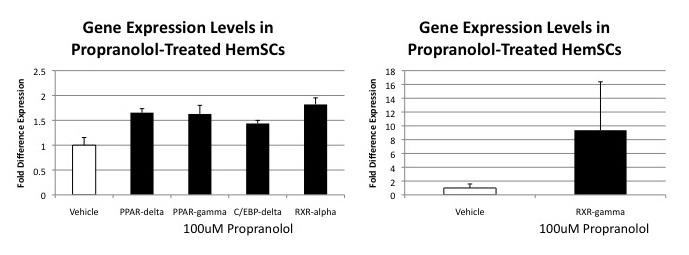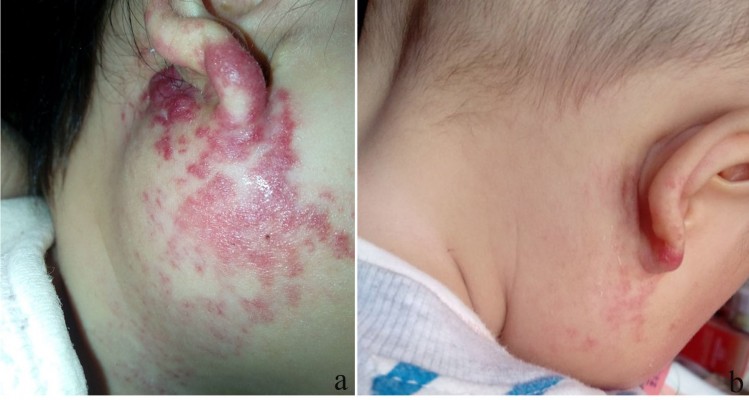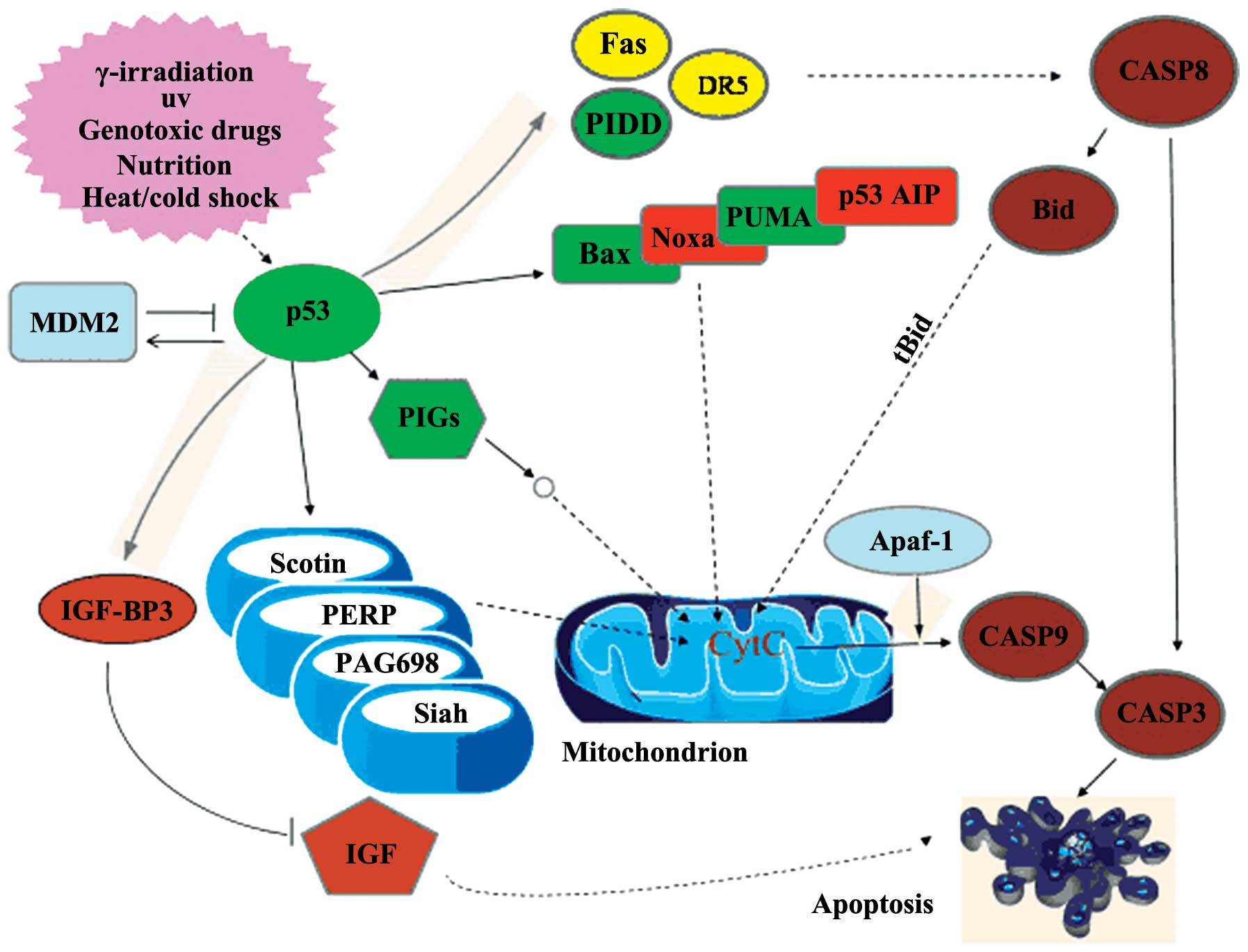
Pingyangmycin stimulates apoptosis in human hemangioma‑derived endothelial cells through activation of the p53 pathway
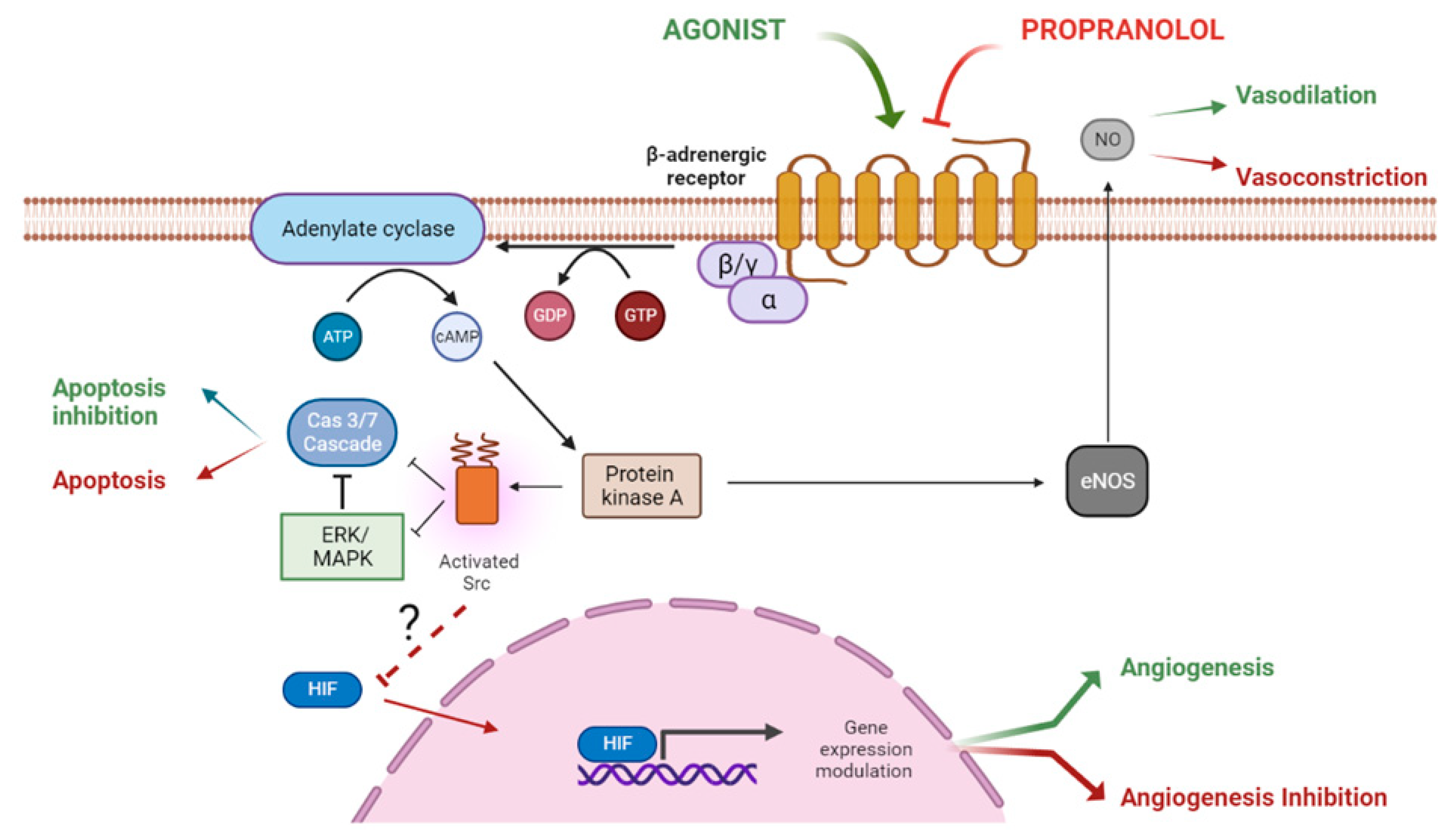
JCM | Free Full-Text | Propranolol: A “Pick and Roll” Team Player in Benign Tumors and Cancer Therapies
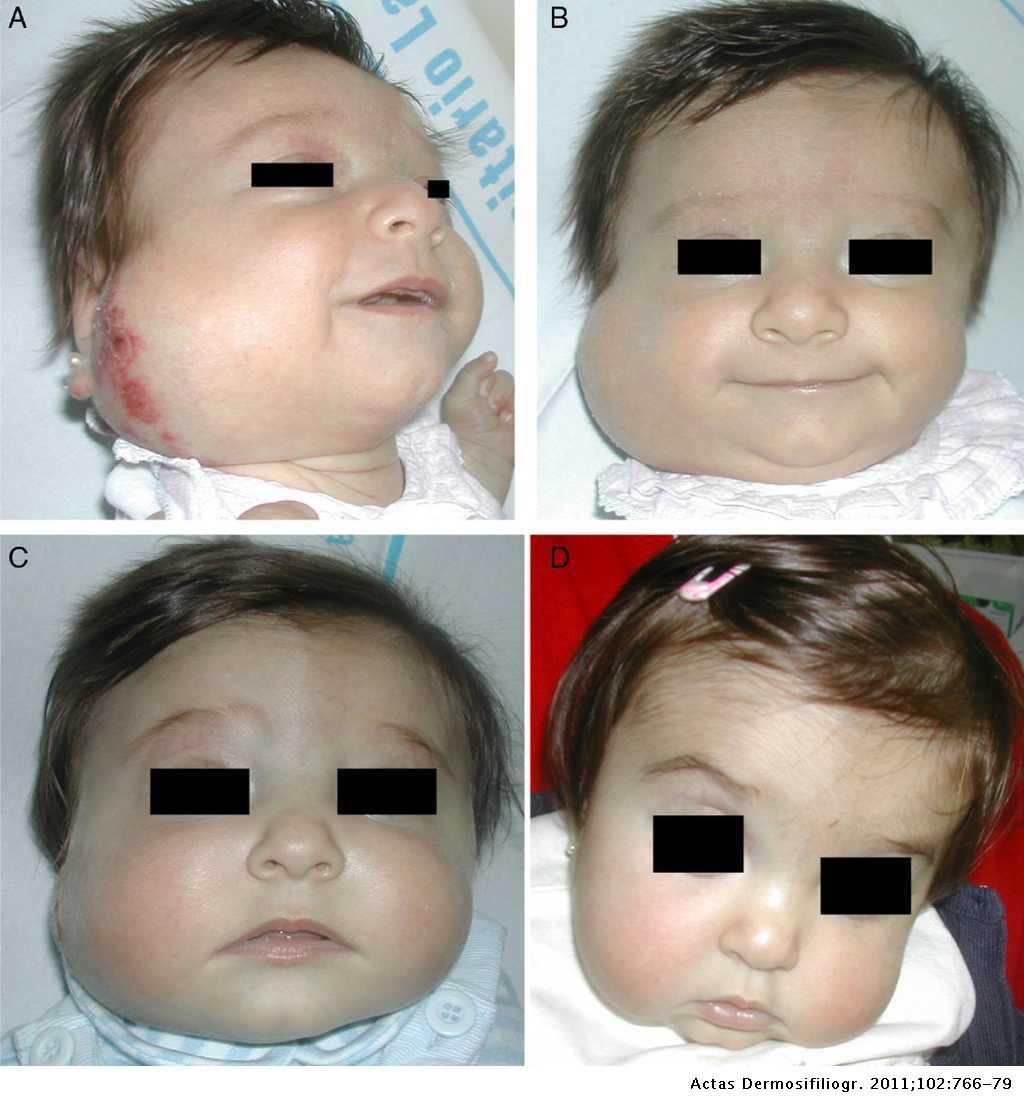
Propranolol in the treatment of infantile hemangioma: clinical effectiveness, risks, and recommendations | Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas

Propranolol Reduces the Development of Lesions and Rescues Barrier Function in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations | Stroke

JCI - Non–beta blocker enantiomers of propranolol and atenolol inhibit vasculogenesis in infantile hemangioma

Propranolol Participates in the Treatment of Infantile Hemangioma by Inhibiting HUVECs Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Tube Formation

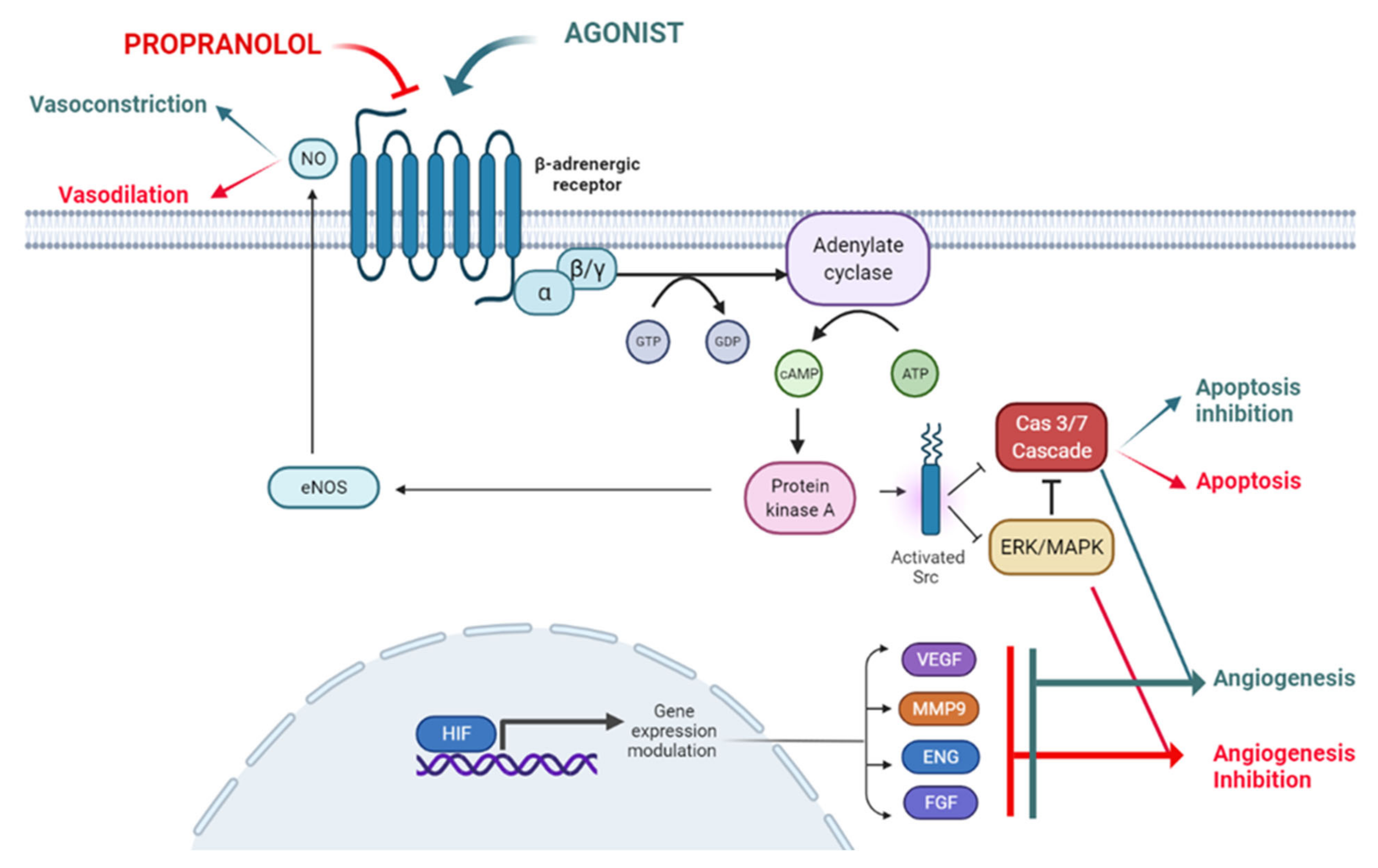
Possible mechanisms of action of propranolol in infantile hemangiomas... | Download Scientific Diagram
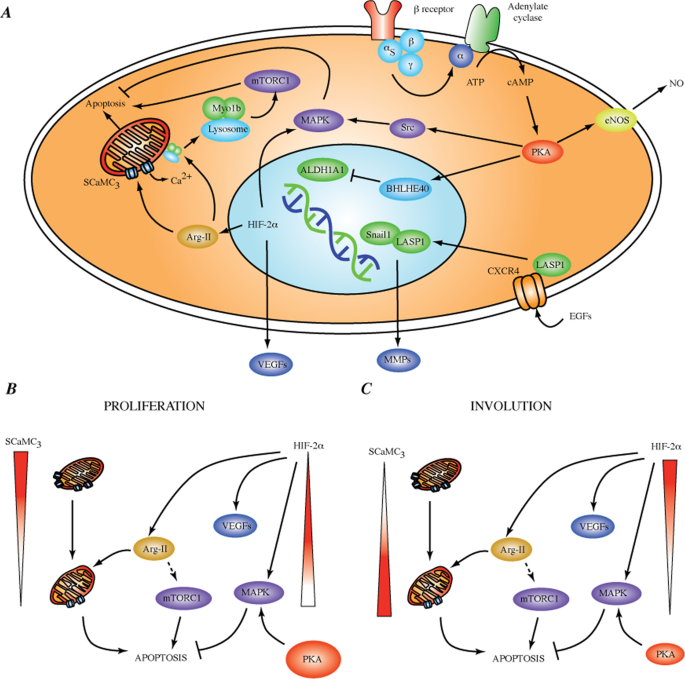
Identification of putative biomarkers for Infantile Hemangiomas and Propranolol treatment via data integration | Scientific Reports

The use of propranolol in the treatment of infantile haemangiomas: an update on potential mechanisms of action - Ji - 2015 - British Journal of Dermatology - Wiley Online Library

Enhanced skin delivery of propranolol HCl using nonionic surfactant-based vesicles for topical treatment of infantile hemangioma - ScienceDirect
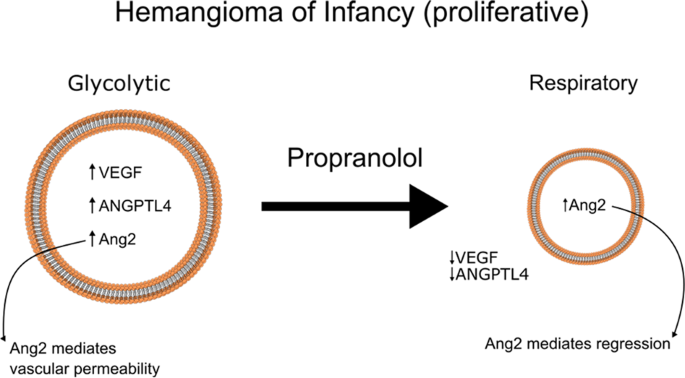
Propranolol exhibits activity against hemangiomas independent of beta blockade | npj Precision Oncology
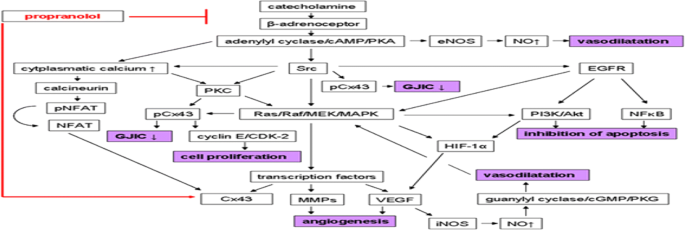
Management of Head and Neck Hemangiomas in Adults: Oral Propranolol Versus Oral Itraconazole in Conjugation with Injection Sodium Tetra Decyl Sulphate | SpringerLink
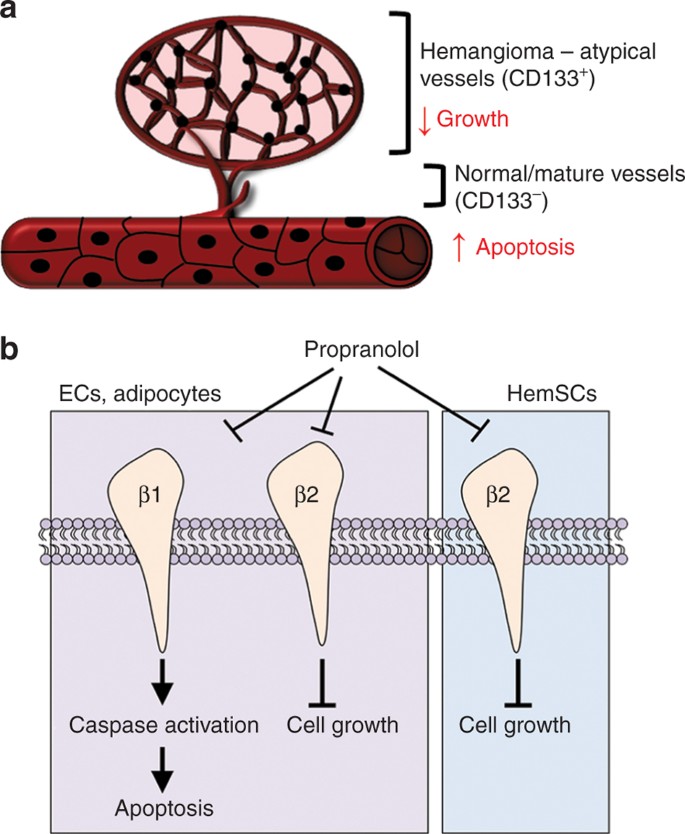
Propranolol inhibits growth of hemangioma-initiating cells but does not induce apoptosis | Pediatric Research

Infantile hemangioma: pathogenesis and mechanisms of action of propranolol - Rotter - 2017 - JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft - Wiley Online Library